Credit Card Processing 101
The credit card processing industry can be very confusing for most merchants, as it involves numerous players. Below are the primary payment processing terms you need to understand, and how they work together to enable credit card transactions.
When an in individual makes an online purchase on a merchant’s website, they will enter their credit/debit card details on a secure webpage (URL being prefixed with “HTTPS”), after which the information is encrypted and sent to either the merchant’s servers, a Payment Service Provider or a payment gateway. Once authorized, the merchant will fulfill the order for the shopper.
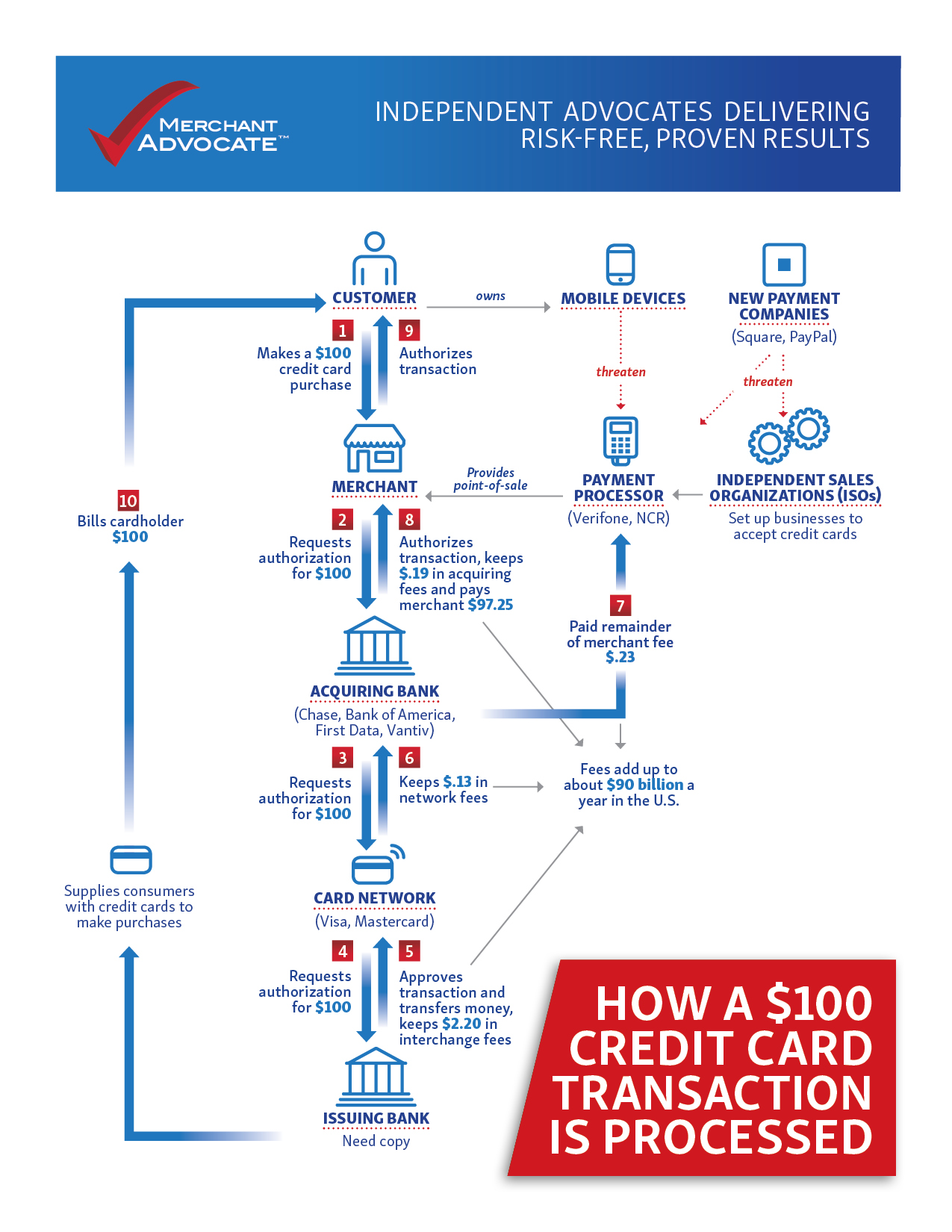
A merchant is an individual or business that wishes to accept credit and debit cards as payment for goods or services. They must work with an acquiring bank to apply for and receive a merchant account. An acquiring bank is a bank or financial institution that is a registered member of a card network, such as Visa or MasterCard, and accepts (or acquires) transactions for merchants on behalf of the debit and credit card networks.
A merchant account is an account number issued to a merchant by an acquiring bank, to identify the merchant as the owner of the transaction info it sends to the bank, as well as the recipient of the funds from the transactions. Merchant accounts are subject to varying fees, which can be implemented through monthly billing, as a percentage of each transaction, or both.
Payment processors enable merchants to receive debit or credit card payments online by providing a connection to an acquiring bank. These processors perform many functions, such as evaluating whether transactions are valid and approved, using anti-fraud measures to assure that a purchase transaction is initiated by the source it claims to be. Processors are held to standards and regulations organized by credit card associations. These standards include rules regarding fraud, chargebacks, and identity theft.
Payment gateways are software and servers that transmit transaction information to acquiring banks and responses from issuing banks as to whether a transaction is approved or declined. Payment gateways usually charge those who use them a per-transaction fee.
PCI is the set of rules and security standards which must be followed by anyone with access to card information. Security is an integral component of all payment gateways, to protect sensitive data such as credit card numbers against fraudulent activities.
Payment Service Providers partner with acquiring banks and their payment processors to offer merchants the capability to accept payments. They often offer services in addition to processing transactions, including PCI compliance, fraud protection and the ability to process different currencies and translate different languages.
An issuing bank is responsible for any cardholder’s ability to pay off the debt they accumulate with the credit card or line of credit given by the bank. Upon receiving a card authorization request, the issuing bank will either approve or decline the transaction, depending on the shopper’s financial situation.
Acquirers/Acquiring banks are registered members of a card network (MasterCard or Visa) and accept or acquire transactions on behalf of those debit and credit card networks for a merchant. The card network connects acquiring banks to issuing banks so that a customer transaction can be verified. Whenever a cardholder uses a debit or credit card for a purchase, the acquiring bank will either approve or decline the transactions based on the information the card network and issuing bank have on record about that card holder’s account. In addition to managing transactions, an acquirer also assumes full risk and responsibility associated with the transactions it processes. The acquirer charges a fee for its service, which may vary and are commonly assessed for activities such as transactions, refunds and chargebacks.
Interchange refers to the clearing and settlement of records between payment system participants. The term can also be used to describe the fees or transfer pricing between issuers and acquirers. Participating acquirers and issuers pay or receive interchange each time a credit or debit card is used. This fee tends to be paid by the acquiring bank or the merchant’s bank to the consumer’s banks or the issuing bank.
Once all authorizations have been made and approvals received by all involved parties, the issuing bank of the shopper sends funds to the seller’s acquiring bank, via that bank’s payment processor. The acquiring bank will then take those funds and deposit them in the merchant’s account. This is called a settlement pay or settlement. For typical card transactions, even though the authorization and approval for order fulfillment take only seconds, the whole payment processing circuit in the background can take up to three days to be completed.